- Miscellaneous
- AM1638, a GPR40-Full Agonist, Inhibited Palmitate- Induced ROS Production and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Enhancing HUVEC Viability in an NRF2-Dependent Manner
-
Hwan-Jin Hwang, Joo Won Kim, SukHwan Yun, Min Jeong Park, Eyun Song, Sooyeon Jang, Ahreum Jang, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):760-769. Published online November 2, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1774
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
G protein-coupled receptor 40 (GPR40) is a key molecule in diabetes and fatty liver, but its role in endothelial dysfunction remains unclear. Our objective in this study was to determine whether GPR40 agonists protect endothelial cells against palmitatemediated oxidative stress.
Methods
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were used to investigate effects of various GPR40 agonists on vascular endothelium.
Results
In HUVECs, AM1638, a GPR40-full agonist, enhanced nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 (NRF2) translocation to the nucleus and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) expression, which blocked palmitate-induced superoxide production. Those antioxidant effects were not detected after treatment with LY2922470 or TAK875, GPR40-partial agonists, suggesting that GPR40 regulates reactive oxygen species (ROS) removal in a ligand-dependent manner. We also found that palmitate-induced CCAAT/enhancer‐binding protein homologous protein expression; X-box binding protein-1 splicing, nuclear condensation, and fragmentation; and caspase-3 cleavage were all blocked in an NRF2-dependent manner after AM1638 treatment. Both LY2922470 and TAK875 also improved cell viability independent of the NRF2/ROS pathway by reducing palmitate-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress and nuclear damage. GPR40 agonists thus have beneficial effects against palmitate in HUVECs. In particular, AM1638 reduced palmitate-induced superoxide production and cytotoxicity in an NRF2/HO-1 dependent manner.
Conclusion
GPR40 could be developed as a good therapeutic target to prevent or treat cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis.
- Thyroid
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database)
- Risk of Diabetes in Patients with Long-Standing Graves’ Disease: A Longitudinal Study
-
Eyun Song, Min Ji Koo, Eunjin Noh, Soon Young Hwang, Min Jeong Park, Jung A Kim, Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Geum Joon Cho, Hye Jin Yoo
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(6):1277-1286. Published online December 16, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1251
-
-
5,231
View
-
181
Download
-
9
Web of Science
-
10
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
The detrimental effects of excessive thyroid hormone on glucose metabolism have been widely investigated. However, the risk of diabetes in patients with long-standing hyperthyroidism, especially according to treatment modality, remains uncertain, with few longitudinal studies.
Methods
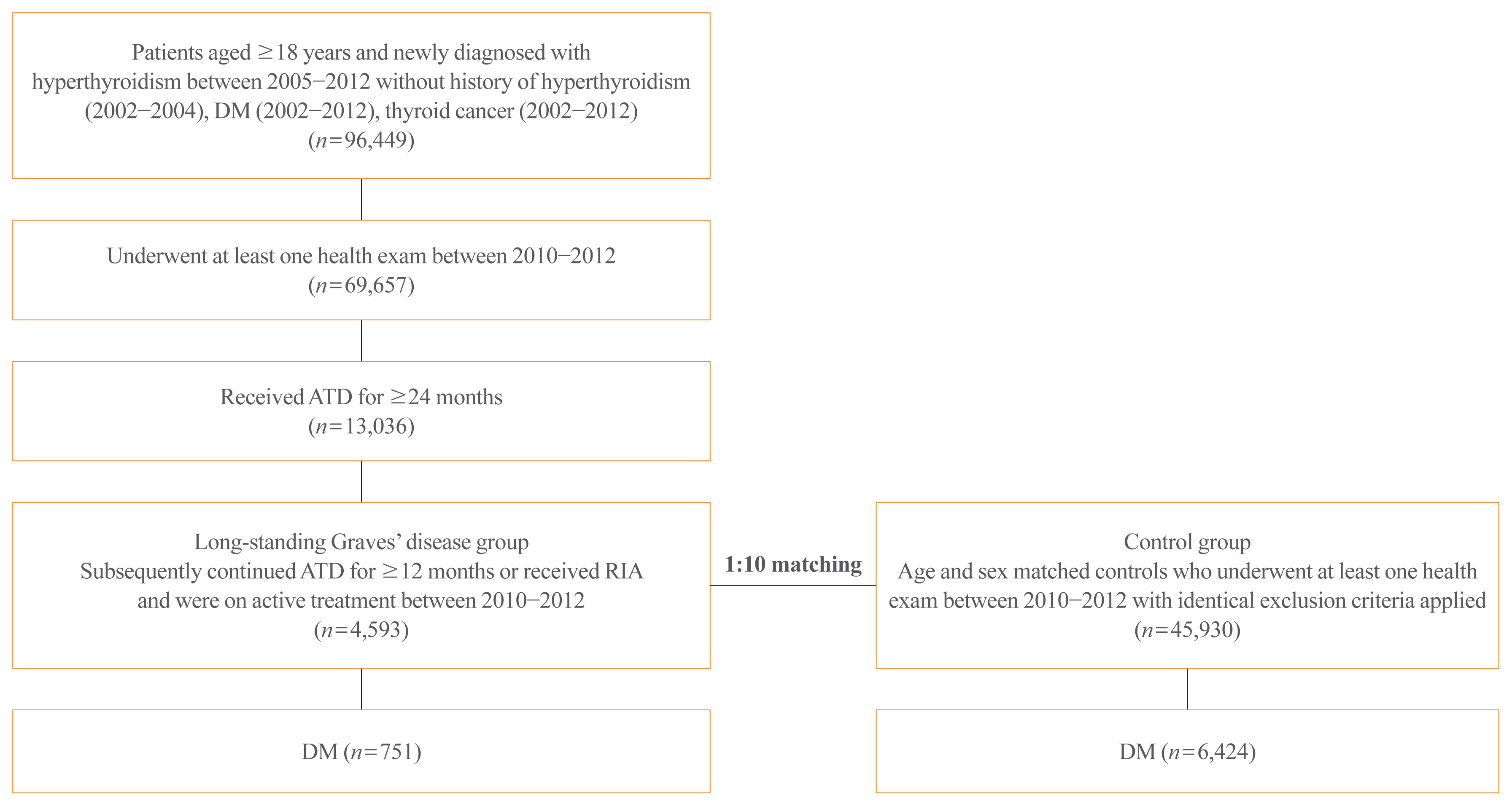
The risk of diabetes in patients with Graves’ disease treated with antithyroid drugs (ATDs) for longer than the conventional duration (≥2 years) was compared with that in age-and sex-matched controls. The risk was further compared according to subsequent treatment modalities after a 24-month course of ATD: continuation of ATD (ATD group) vs. radioactive iodine ablation (RIA) group.
Results
A total of 4,593 patients were included. Diabetes was diagnosed in 751 (16.3%) patients over a follow-up of 7.3 years. The hazard ratio (HR) for diabetes, after adjusting for various known risk factors, was 1.18 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.10 to 1.28) in patients with hyperthyroidism. Among the treatment modality groups, the RIA group (n=102) had a higher risk of diabetes than the ATD group (n=4,491) with HR of 1.56 (95% CI, 1.01 to 2.42). Further, the risk of diabetes increased with an increase in the ATD treatment duration (P for trend=0.019).
Conclusion
The risk of diabetes was significantly higher in patients with long-standing Graves’ disease than in the general population, especially in patients who underwent RIA and prolonged ATD treatment. Special attention to hyperglycemia during follow-up along with effective control of hyperthyroidism may be necessary to reduce the risk of diabetes in these patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Safety of non-standard regimen of systemic steroid therapy in patients with Graves’ orbitopathy: a single-centre experience
Nadia Sawicka-Gutaj, Dawid Gruszczyński, Natalia Zawalna, Kacper Nijakowski, Agnieszka Skiba, Mateusz Pochylski, Jerzy Sowiński, Marek Ruchała
Pharmacological Reports.2024; 76(1): 185. CrossRef - Increased risk of diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer
Hwa Young Ahn, Jooyoung Lee, Jinmo Kang, Eun Kyung Lee
European Journal of Endocrinology.2024; 190(3): 248. CrossRef - Prevalencia de diabetes en personas con disfunción tiroidea
Juan J. Díez, Pedro Iglesias
Medicina Clínica.2023; 160(8): 333. CrossRef - Control of Thyroid Dysfunction in Spanish Population Registered in
the Primary Care Clinical Database: An Analysis of the Proportion of Patients
with Thyrotropin Values Outside the Reference Range
Juan J. Díez, Pedro Iglesias
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2023; 55(03): 184. CrossRef - Prevalence of thyroid dysfunction and its relationship to income level and employment status: a nationwide population-based study in Spain
Juan J. Díez, Pedro Iglesias
Hormones.2023; 22(2): 243. CrossRef - Prevalence of diabetes in people with thyroid dysfunction
Juan J. Díez, Pedro Iglesias
Medicina Clínica (English Edition).2023; 160(8): 333. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus Secondary to Endocrine Diseases: An Update of Diagnostic and Treatment Particularities
Mihaela Simona Popoviciu, Lorena Paduraru, Raluca Marinela Nutas, Alexandra Maria Ujoc, Galal Yahya, Kamel Metwally, Simona Cavalu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(16): 12676. CrossRef - Thyroid Eye Disease and Its Association With Diabetes Mellitus: A Major Review
Roshmi Gupta, Pramila Kalra, Lakshmi B. Ramamurthy, Suryasnata Rath
Ophthalmic Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery.2023; 39(6S): S51. CrossRef - Metabolite Changes during the Transition from Hyperthyroidism to Euthyroidism in Patients with Graves’ Disease
Ho Yeop Lee, Byeong Chang Sim, Ha Thi Nga, Ji Sun Moon, Jingwen Tian, Nguyen Thi Linh, Sang Hyeon Ju, Dong Wook Choi, Daiki Setoyama, Hyon-Seung Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 891. CrossRef - Diabetes and Hyperthyroidism: Is There a Causal Link?
Sang Yong Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(6): 1175. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Gender-Dependent Reference Range of Serum Calcitonin Levels in Healthy Korean Adults
-
Eyun Song, Min Ji Jeon, Hye Jin Yoo, Sung Jin Bae, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Hong-Kyu Kim, Won Gu Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(2):365-373. Published online April 7, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.939
-
-
5,071
View
-
152
Download
-
4
Web of Science
-
5
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
Serum calcitonin measurement contains various clinical and methodological aspects. Its reference level is wide and unclear despite sensitive calcitonin kits are available. This study aimed to identify the specific reference range in the healthy Korean adults.
Methods
Subjects were ≥20 years with available calcitonin (measured by a two-site immunoradiometric assay) data by a routine health checkup. Three groups were defined as all eligible subjects (group 1, n=10,566); subjects without self or family history of thyroid disease (group 2, n=5,152); and subjects without chronic kidney disease, autoimmune thyroid disease, medication of proton pump inhibitor/H2 blocker/steroid, or other malignancies (group 3, n=4,638).
Results
This study included 6,341 male and 4,225 female subjects. Males had higher mean calcitonin than females (2.3 pg/mL vs. 1.9 pg/mL, P<0.001) in group 1. This gender difference remained similar in groups 2 and 3. Calcitonin according to age or body mass index was not significant in both genders. Higher calcitonin in smoking than nonsmoking men was observed but not in women. Sixty-nine subjects had calcitonin higher than the upper reference limit (10 pg/mL) and 64 of them had factors associated with hypercalcitoninemia besides medullary thyroid cancer. Our study suggests the reference intervals for men who were non, ex-, current smokers, and women (irrespective of smoking status) as <5.7, <7.1, <7.9, and <3.6 pg/mL, respectively.
Conclusion
Specific calcitonin reference range should be provided considering for sex and smoking status. Taking account for several factors known to induce hypercalcitoninemia can help interpret the gray zone of moderately elevated calcitonin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Determinants of circulating calcitonin value: analysis of thyroid features, demographic data, anthropometric characteristics, comorbidities, medications, and smoking habits in a population with histological full exclusion of medullary thyroid carcinoma
Pierpaolo Trimboli, Giuseppe Peloni, Dorotea Confalonieri, Elena Gamarra, Tommaso Piticchio, Francesco Frasca, Petra Makovac, Arnoldo Piccardo, Lorenzo Ruinelli
Frontiers in Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Surgical treatment of solid variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma: Fifteen-year experience of a tertiary center
Katarina Tausanović, Marina Stojanović, Milan Jovanović, Boban Stepanović, Jovan Ilić, Sara Ivaniš, Vladan Živaljević
Medicinska istrazivanja.2024; 57(1): 121. CrossRef - Some genetic differences in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Hosam M. Ahmad, Zaki M. Zaki, Asmaa S. Mohamed, Amr E. Ahmed
BMC Research Notes.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Presence or severity of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis does not influence basal calcitonin levels: observations from CROHT biobank
M. Cvek, A. Punda, M. Brekalo, M. Plosnić, A. Barić, D. Kaličanin, L. Brčić, M. Vuletić, I. Gunjača, V. Torlak Lovrić, V. Škrabić, V. Boraska Perica
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2022; 45(3): 597. CrossRef - Environmental Factors That Affect Parathyroid Hormone and Calcitonin Levels
Mirjana Babić Leko, Nikolina Pleić, Ivana Gunjača, Tatijana Zemunik
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 23(1): 44. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Clinical Outcomes after Early and Delayed Radioiodine Remnant Ablation in Patients with Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Propensity Score Matching Analysis
-
Jonghwa Ahn, Meihua Jin, Eyun Song, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Jin-Sook Ryu, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Ji Min Han, Won Gu Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(4):830-837. Published online November 18, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.747
-
-
4,279
View
-
132
Download
-
3
Web of Science
-
6
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
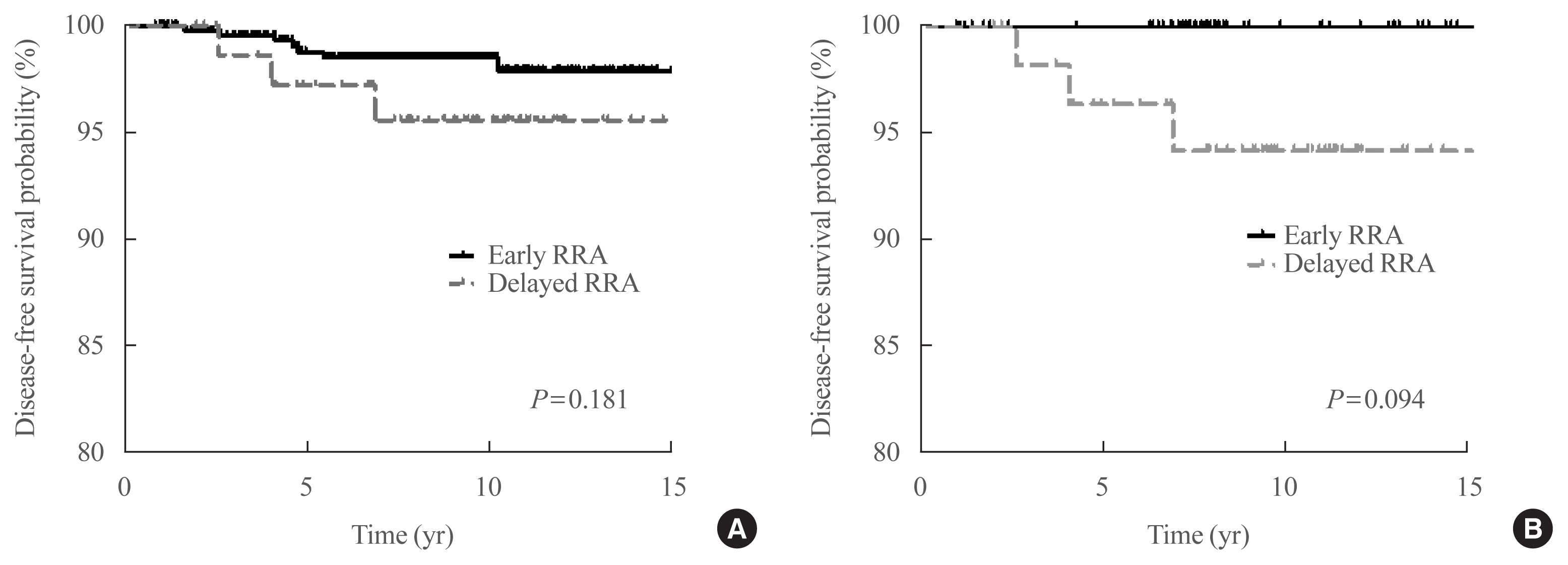
The clinical outcomes of delayed radioiodine remnant ablation (RRA) therapy in patients with low-risk papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) are unclear. We aimed to evaluate the clinical impact of the interval between total thyroidectomy (TT) and RRA therapy in patients with low-risk PTC.
Methods
We included 526 patients who underwent TT and RRA for low-risk PTC with a primary tumor size of >1 cm between 2000 and 2012. Patients were divided into the early (<90 days) and the delayed (≥90 days) RRA groups based on the interval between TT and RRA. The results of diagnostic whole-body scan (DxWBS), ongoing risk stratification (ORS; response to therapy), and disease-free survival (DFS) were evaluated before and after propensity score matching (PSM).
Results
Among the 526 patients, 75 (14.3%) patients underwent delayed RRA; they had more cervical lymph node metastasis and received a higher RRA dose than those who underwent early RRA. The median follow-up period was 9.1 years after initial therapy, and the structural recurrence rate was 1.9%. In DxWBS, 60 patients had focal iodine uptake limited in operative bed, with no significant difference between groups. According to ORS, 78%, 20%, 1%, and 1% patients were classified into excellent, indeterminate, biochemical incomplete, and structural incomplete response groups, respectively. There was no significant difference in ORS or DFS between groups before and after PSM.
Conclusion
The timing of the first RRA had no clinical impact in patients with low-risk PTC. Thus, the clinical decision for RRA can be determined >3 months after TT considering other prognostic factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Dynamic risk assessment in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer
Erika Abelleira, Fernando Jerkovich
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2024; 25(1): 79. CrossRef - Ablation Rates and Long-Term Outcome Following Low-Dose Radioiodine for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer in the West of Scotland: A Retrospective Analysis
Kathryn Graham, Fay Tough, Helena Belikova, Irene Wotherspoon, David Colville, Nicholas Reed
Endocrine Practice.2024; 30(4): 327. CrossRef - Radioiodine ablation after thyroidectomy could be safely abandoned or postponed in selected stage I papillary thyroid carcinoma patients of low-risk group: an observational prospective study
S.M. Cherenko, A.Yu. Glagolieva, D.E. Makhmudov
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2024; 20(1): 7. CrossRef - Patient Preparation and Radiation Protection Guidance for Adult Patients Undergoing Radioiodine Treatment for Thyroid Cancer in the UK
J. Wadsley, N. Armstrong, V. Bassett-Smith, M. Beasley, R. Chandler, L. Cluny, A.J. Craig, K. Farnell, K. Garcez, N. Garnham, K. Graham, A. Hallam, S. Hill, H. Hobrough, F. McKiddie, M.W.J. Strachan
Clinical Oncology.2023; 35(1): 42. CrossRef - Delay of initial radioactive iodine therapy beyond 3 months has no effect on clinical responses and overall survival in patients with thyroid carcinoma: A cohort study and a meta‐analysis
Fang Cheng, Juan Xiao, Fengyan Huang, Chunchun Shao, Shouluan Ding, Canhua Yun, Hongying Jia
Cancer Medicine.2022; 11(12): 2386. CrossRef - Delayed (>3 Months) Postoperative Radioactive Iodine Ablation Does Not Impact Clinical Response or Survival in Differentiated Thyroid Cancers
Tatiana Fedorova, Lilah F. Morris-Wiseman
Clinical Thyroidology.2022; 34(10): 456. CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- Quality of Life in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma According to Treatment: Total Thyroidectomy with or without Radioactive Iodine Ablation
-
Jonghwa Ahn, Min Ji Jeon, Eyun Song, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):115-121. Published online March 19, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.115
-
-
5,541
View
-
110
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
12
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
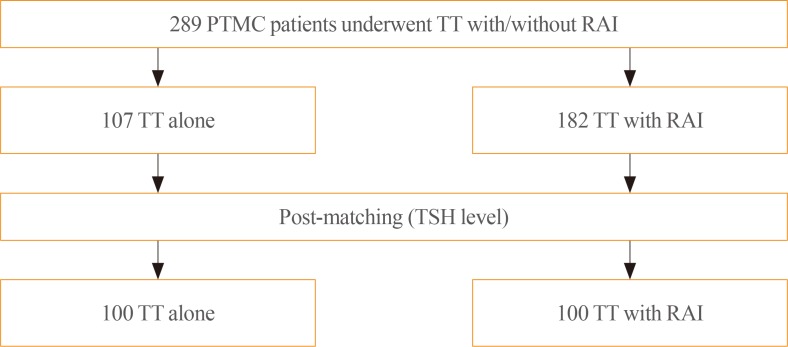
Recently, there has been some controversy regarding the role of radioactive iodine (RAI) ablation in the treatment of low-risk differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC), especially papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (PTMC). This study aimed to compare quality of life (QoL) parameters between patients with PTMC who underwent total thyroidectomy (TT) alone and those who underwent TT with RAI ablation. MethodsIn this cross-sectional study, patients with PTMC who underwent TT with/without RAI remnant ablation were prospectively enrolled between June 2016 and October 2017. All patients completed three questionnaires: the 12-item short-form health survey (SF-12), thyroid cancer-specific quality of life (THYCA-QoL) questionnaire, and fear of progression (FoP) questionnaire. ResultsThe TT and TT with RAI groups comprised 107 and 182 patients, respectively. The TT with RAI group had significantly lower serum thyrotropin (TSH) levels than the TT group. However, after matching for TSH levels between the groups (n=100 in both groups), there were no significant differences in baseline characteristics. According to the SF-12, the score for general health was significantly lower in the TT with RAI group than in the TT group (P=0.047). The THYCA-QoL also showed a significant difference in the “felt chilly” score between groups (P=0.023). No significant differences in FoP scores were observed between the groups. ConclusionPatients with PTMC who underwent TT with RAI ablation experienced more health-related problems than those managed with TT alone. These findings support the idea that RAI ablation should be carefully considered in patients with low-risk DTCs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Quality of life of patients with thyroid cancer in Colombia
Oscar Gómez, Alvaro Sanabria
Endocrinología, Diabetes y Nutrición.2024; 71(2): 61. CrossRef - Quality of life of patients with thyroid cancer in Colombia
Oscar Gómez, Alvaro Sanabria
Endocrinología, Diabetes y Nutrición (English ed.).2024; 71(2): 61. CrossRef - Fear of Cancer Recurrence in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review
Jacob Hampton, Ahmad Alam, Nicholas Zdenkowski, Christopher Rowe, Elizabeth Fradgley, Christine J. O'Neill
Thyroid®.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Review: Improving quality of life in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer
Pia Pace-Asciak, Jonathon O. Russell, Ralph P. Tufano
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-Related Quality of Life and Thyroid Cancer-Specific Symptoms in Patients Treated for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: A Single-Center Cross-Sectional Survey from Mainland China
Changlian Chen, Jiayan Cao, Yueyang Wang, Xuya Han, Yaju Zhang, Shumei Zhuang
Thyroid.2023; 33(4): 474. CrossRef - The "not so good" thyroid cancer: a scoping review on risk factors associated with anxiety, depression and quality of life
Kyle Alexander, Sum-Yu Christina Lee, Stelios Georgiades, Constantina Constantinou
Journal of Medicine and Life.2023; 16(3): 348. CrossRef - Comparison of health‐related quality of life and cosmetic outcome between traditional gasless trans‐axillary endoscopic thyroidectomy and modified gasless trans‐axillary endoscopic thyroidectomy for patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
Deenraj Kush Dhoomun, HuiLan Cai, Ning Li, YanHuan Qiu, XingRui Li, XiaoPeng Hu, WenZhuang Shen
Cancer Medicine.2023; 12(15): 16604. CrossRef - Risk of Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes in Young Women with Thyroid Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Shinje Moon, Ka Hee Yi, Young Joo Park
Cancers.2022; 14(10): 2382. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life following FDG-PET/CT for cytological indeterminate thyroid nodules
Elizabeth J de Koster, Olga Husson, Eveline W C M van Dam, G Sophie Mijnhout, Romana T Netea-Maier, Wim J G Oyen, Marieke Snel, Lioe-Fee de Geus-Oei, Dennis Vriens, _ _
Endocrine Connections.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Is a four-week hormone suspension necessary for thyroid remnant ablation in low and intermediate risk patients? A pilot study with quality-of-life assessment
Poliane A.L. Santos, Maria E.D.M. Flamini, Felipe A. Mourato, Fernando R.A. Lima, Joelan A.L. Santos, Fabiana F. Lima, Estelita T.B. Albuquerque, Alexandra C. De Freitas, Simone C.S. Brandão
Brazilian Journal of Radiation Sciences.2022; 10(4): 1. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life after transoral robotic thyroidectomy in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Chang Myeon Song, Hyang Sook Bang, Hyung Gu Kim, Hae Jin Park, Kyung Tae
Surgery.2021; 170(1): 99. CrossRef - Protocol for a Korean Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study of Active Surveillance or Surgery (KoMPASS) in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
Min Ji Jeon, Yea Eun Kang, Jae Hoon Moon, Dong Jun Lim, Chang Yoon Lee, Yong Sang Lee, Sun Wook Kim, Min-Hee Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Minho Shong, Sun Wook Cho, Won Bae Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(2): 359. CrossRef
|